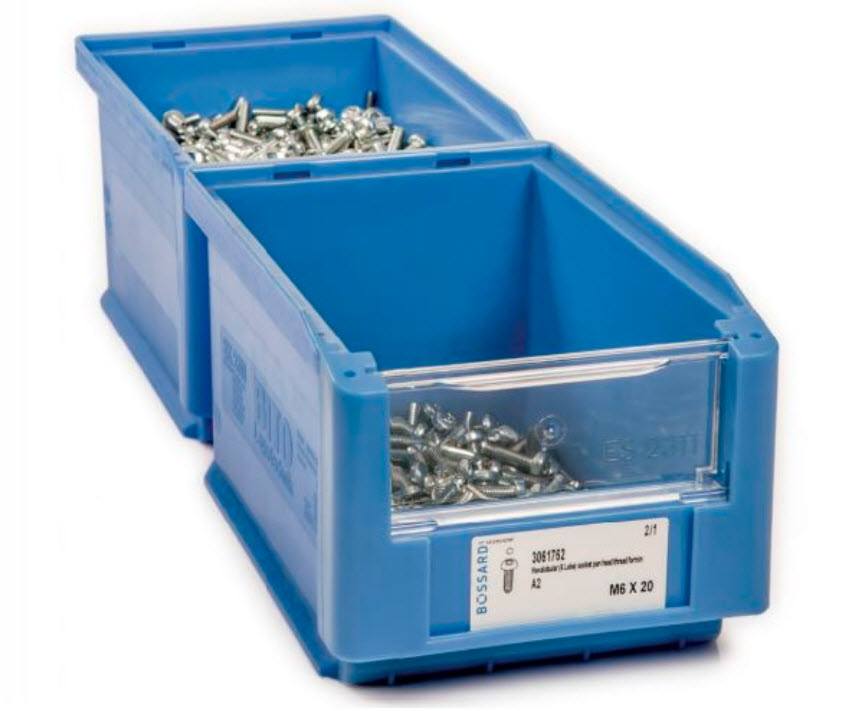
A two bin system is a simple, visually-based method for stocking and replacing items that is used. It is common on assembly and moving production lines where elements units are added to the merchandise. One bin is the working bin, where items for manufacture and sale are taken from. When the first container gets empty, it means time to refill. But when it is refilling, the second container with elements is used in work.
It is merely like its name suggests, it’s composed of 2 bins that area unit filled with elements or materials to start out. As production starts one bin is drawn down of materials and therefore the alternative bin, it’s going to fill the act of safety stock. It works well for ordering everything from specific product inventory items to consumable supplies, including office products.
We have to keep the EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) and Kanban in mind while maintaining the two bin inventory system. EOQ is the order quantity that minimizes the total holding costs and ordering costs. Kanban signals and maintain an inventory level. Kanban cards are sent to produce and deliver new shipment as the material is consumed.
When Does the Two Bin System Work?
The two bins system workes best when criteria’s are met which makes it more efficient:
- The product is not expensive so that stock easily can be maintained.
- Time management of replenishing stock should be less than consuming.
Advantages of Two Bin System
- Prevents running out of stock
- Triggered for replenishment
- Managed in lead time
- Meet the demand of customers
- Pooled risk
- Spreads inventory throughout the plant
- Manage the disaster span
Disadvantages of Two Bin System
- Inventory level is high
- More investment
- Increase costing due to high-level demand
- Spend more to get insured
- Other expenses to manage extra stock
Two Bin Inventory Control
Two-bin inventory control is an inventory control system used to determine when materials used in production should be replenished. This control method is mainly used for low-value items like when working stock has depleted, an order is placed to replace these things and second bin is supposed to have enough products to last until the replaced order arrives. The first container has a minimum of working stock and the second container keeps reserve stock. Bin cards and store ledger cards are used to record the inventory.
Break down of inventory
A company’s stock is one of its most valuable assets. In retail, manufacturing, food service and other inventory intensive sectors, a company’s inputs and finished products are the core of its business, and a shortage of stock when and where it’s needed can be extremely detrimental. At the same time, the stock can be a liability. An extensive inventory carries the risk of spoilage, theft, damage, or shifts in demand. Stock must be insured, and if it is not selling in time, it may have to dispose at clearance prices.
Days Sale of Inventory
The day’s sales of inventory value measure the company’s inventory into sales which also gives investors an idea of how long it takes a group to turn its inventory into sales. Usually, a lower DSI is preferred. Two bin inventory system works with the interaction of DSI which we have to maintain according to the industry.
Inventory Turnover
The inventory turnover refers to the number of times that inventory is sold or used over the course of a particular period such as a quarter or year. It’s a metric to measure a company’s efficiency regarding management, inventory, and generation of sales. The higher inventory turnover ratio, the better it is for the company, as it indicates a higher production of sales and vice versa, but it also depends on the demand for the product. Two bin inventory systems would be maintained by this turnover too. Every factor will matter in the inventory management system.
Why the Sales of Inventory Matter in Two Bins Inventory Management
Metrics such as inventory turnover and days sales of inventory can help inform investment decisions as they indicate to an investor whether a company can efficiently manage its stock when compared to competitors. All these correlations seem intuitive; it is important to note possible exceptions. Sometimes, low inventory ratio may be preferred, for instance, if inventory increased in anticipation of a market shortage or a rapid price increase. If the stock is selling slowly, then a surplus is probably not desirable. On the other hand, a lack of inventory can lead to a higher turnover ratio, though the company may experience a loss of sales. It is essential to find a mutually beneficial balance between optimal inventory levels and market demand.