In our life, we often come across a point where we have to make a tough decision for ourselves such as starting a new chapter or embrace a change. At that point, we sometimes find ourselves helpless, clueless and with no solution to the problem. While assessing if and but’s of the situation, we need a systematic technique of decision making to enhance the chance of success. Force Field Analysis is a tool used for the process of such decision making. So, what is Force Field Analysis and how does it help in decision making when implementing a change?
Force Field Analysis and Mechanism of Analysis
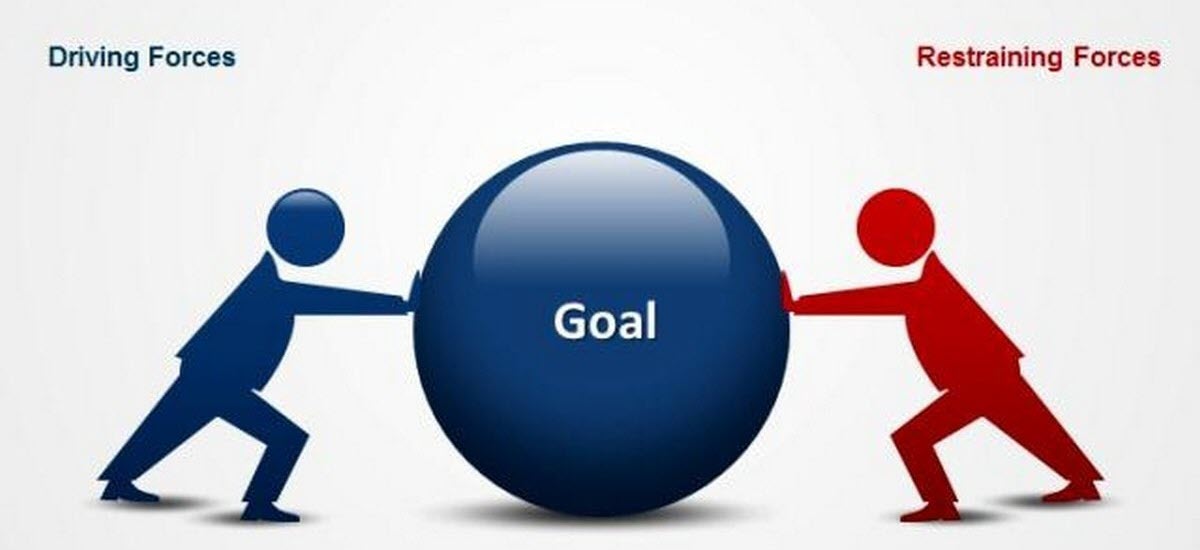
Developed by German-American Social psychologist Kurt Lewin, Force Field Analysis is a tool that assesses driving and restraining forces (agents) in the process of implementing a change. According to Kurt Lewin: “An issue is held in equilibrium by two opposing forces, one that is seeking change (Driving Force) and the other that is resisting the change (Restraining Force).”
According to Kurt Lewin, any given situation is kept at equilibrium by the sum of forces driving change, and the forces resisting the change. To change a given situation, driving forces must be strengthened or restraining forces must be weakened.
Driving Forces
Driving forces are positive forces that point energy towards achieving the objective or goal. They are the stimuli to facilitate change. Examples of this include, but is not limited to:
- Customer’s Feedback
- Invention
- Praise by employer
- A vacant post
- A new opportunity
- Market shift
- A new law that is beneficial
- Sponsors
Restraining Forces
Restraining forces are negative forces that restrict the activity from achieving the objective or goal. The act to decrease the effect of driving forces. Thus, limiting the possibility of a change. Examples of those are, bur is not limited to:
- Fear of failure
- Lack of courage
- Hostile environment
- Shortage of resources
- Market depression
- Negative remarks/feedback
Shifting the Equilibrium
For a successful shift towards change, do the following
- Build Up Driving Forces
- Decrease Restraining Forces
- Or both
According to Lewin, the desired objective or goal is achieved by three steps
- Disintegrate the driving and restraining forces from the state of the status quo.
- Shift the equilibrium in favor of change by applying the above three steps.
- Reintegrate the driving and restraining forces, once the goal is achieved.
Step by Step Guide: How to Apply the Force Field Analysis
As we discussed earlier, Lewin’s change management tool is used to analyze the driving and restraining forces in the process of bringing about change. One can analyze and predict the process by applying the following steps:
- Set the Goal or Objective you want to achieve – Write down the present state, and the goal or objective you want to achieve side by side.
- Identify the possible Field Forces – This step requires a lot of brainstorming. Think of the problem, resources, strengths, and weaknesses. Consult with your colleagues, friends, and family. The simple methods to do it your self are by doing SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and Threat) analysis or PRIMO-F (People, Resources, Innovation, Marketing, Operations, and Finance) analysis. For personal decisions use SWOT and for business, related decisions use PRIMO-F.
- Rate the forces at a scale of 5 – After identifying the driving and restraining forces, calculate their intensities by scaling each one of them on a scale of 5. Write down forces on a paper and scale them from 1 to 5 according to their flexibilities.
- Make a Strategy – The next step is deciding to bring about a change or stop the process. If your SWOT or PRIMO-F analysis are encouraging to bring a change, you must go for a change. Plan a strategy to strengthen some driving forces and weakening some restraining forces to achieve the desired goal or objective. Choose those steps that will create the most impact on your goal.
Benefits of using Force Field Analysis
Force Field Analysis is an effective change management tool. It helps us understand the following:
- How societies Adopt Change.
- How fear create resistance towards change.
- A scientific way for decision making.
- How to analyze, assess any situation.
- What the necessary steps are to bring about change.
- Importance of group communication.