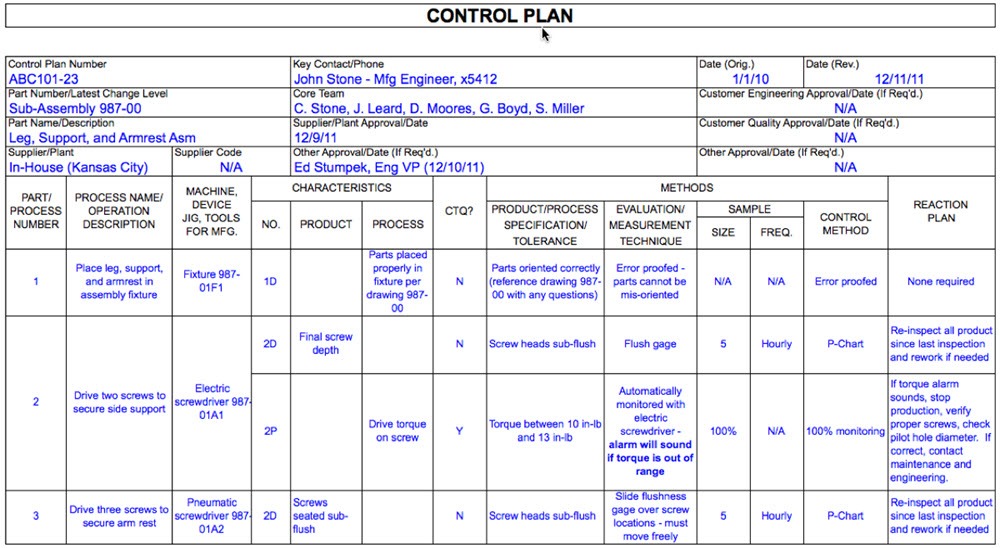
The process Control Plan is a report that depicts the activities (measurements, assessments, quality checks or observing process parameters) required at each section of a process to guarantee the process yields will adjust to pre-decided requirements. In easy words, the process control plan furnishes the inspector or operators with the data required to legitimately control the process and create quality parts or products. It should likewise incorporate directions in regards to action taken if a non-conformance is distinguished. The control plan does not replace operator guidelines. Now and again the process control plan is used as a part of or in conjunction with a checklist or inspection sheet. Control plans are documents that should periodically be updated as the measurement and controls are enhanced for the duration of the life cycle of the product.
Most organizations are searching for strategies to decrease the cost and elimination of waste in their processes. In the business world today controlling waste and keeping up a top level quality is basic for an organization to succeed. The cost of business is regularly expanding. Increasing expenses of raw materials joined with labor and hardware costs have made scrap reduction critical to businesses. Due to this, it has become more vital to guarantee that parts are being delivered that comply with client requirements and without defects. Furthermore, we should be able to recognize a non-conforming part or assembly and also plan for responding to changing process conditions. The larger parts of manufacturing organizations are experienced at detecting initial problems and creating remedial activities to adjust the issue. Be that as it may, numerous miss the mark with regards to managing those restorative activities or process enhancements over a long time. The process steadily comes back to its previous state and the issues in the end re-emerge. The reason for a process control plan is to screen processes and guarantee that any changes are kept up over the life cycle of the part or product. Control Plans are right now being used to guarantee product quality in the Automotive, Aerospace, Agricultural Equipment, Heavy Equipment and numerous different enterprises all throughout the world. A control plan is frequently a Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) necessity for providers of parts to organizations in these enterprises.
How to Use a Process Control Plan in Manufacturing
The process control plan should be created by a Cross Functional Team (CFT) that has a comprehension of the process being controlled or progressed. By using a CFT, you are probably going to distinguish more open doors for development of the process. The process control plan is something other than a document to fill out. It is a plan created by the group to control the process and guarantee the process produces quality parts that meet the client specification. The data contained in the control plan can start from a few sources, including yet not restricted to the following:
- Process Flow Diagram
- Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA)
- Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA)
- Special Characteristics Matrix
- Lessons Learned from similar parts
- Design Reviews
- Team knowledge about the process
- Field or warranty issues
For the duration of the life cycle of a product, the data contained in the list above changes or the content gradually grows. In this way the control plan must be a living document, constantly updated as new data is included. The process control plan accordingly is an indispensable part of a compelling product quality system.
3 Levels of Process Control Plans
Before finishing the process control plan development, the group must decide the best level proper for the process being controlled. There are three designations for a process control plan level in light of what point the product is at in the New Product Introduction (NPI) process. They are as per the following:
- Prototype – This level Control Plan should incorporate descriptions of the measurements to be estimated and the material and performance tests to be finished amid the prototype build.
- Pre-launch – This level of control plan should contain the descriptions of the measurements to be estimated and the material and performance tests to be finished after prototype, however preceding product launch and normal production.
- Production – This level of Control Plan should contain an extensive listing of the product and process special attributes, the process controls, estimation methods and tests that will be performed amid regular production.